Robust Multimodal Interpretation: Interior Decoration Domain (Gaze)
Overview
In this study, a static 3D bedroom scene is shown to the user. The system verbally asks the user a list of questions one at a time about the bedroom and the user answers the questions by speaking to the system.
- The collected data includes users’ speech and accompanying gaze fixations (with possibly selected objects identified by the system).
- Users’ speech was transcribed.
Datasets
Download
- Data used for Language Processing and Acquisition:
- Data used for Reference Resolution:
Descriptions
-
domain_kb.xmlThe domain model file domain model file that defines the properties of each object.
Each property is annotated with a concept (WordNet synset in the format of
<word>#<pos-tag>#<sense-id>). Each object property also has a list of “gold standard” words. The “gold standard” words are the words that the users have used to refer to the objects and their properties (e.g., color, size, shape) during the interaction with the system. The “gold standard” words are manually compiled from all users' speech transcripts and gaze fixations. An example:<object name="dresser_desk" id="12"> <properties> <type text="dresser#n#4">desk dresser table vanity</type> </properties> </object> ...In the above example, Object
dresser_desk(id=12) has one property:type. The concept of propertytypeisdresser#n#4. The gold standard words for propertytypeare:desk,dresser,talbe,vanity. -
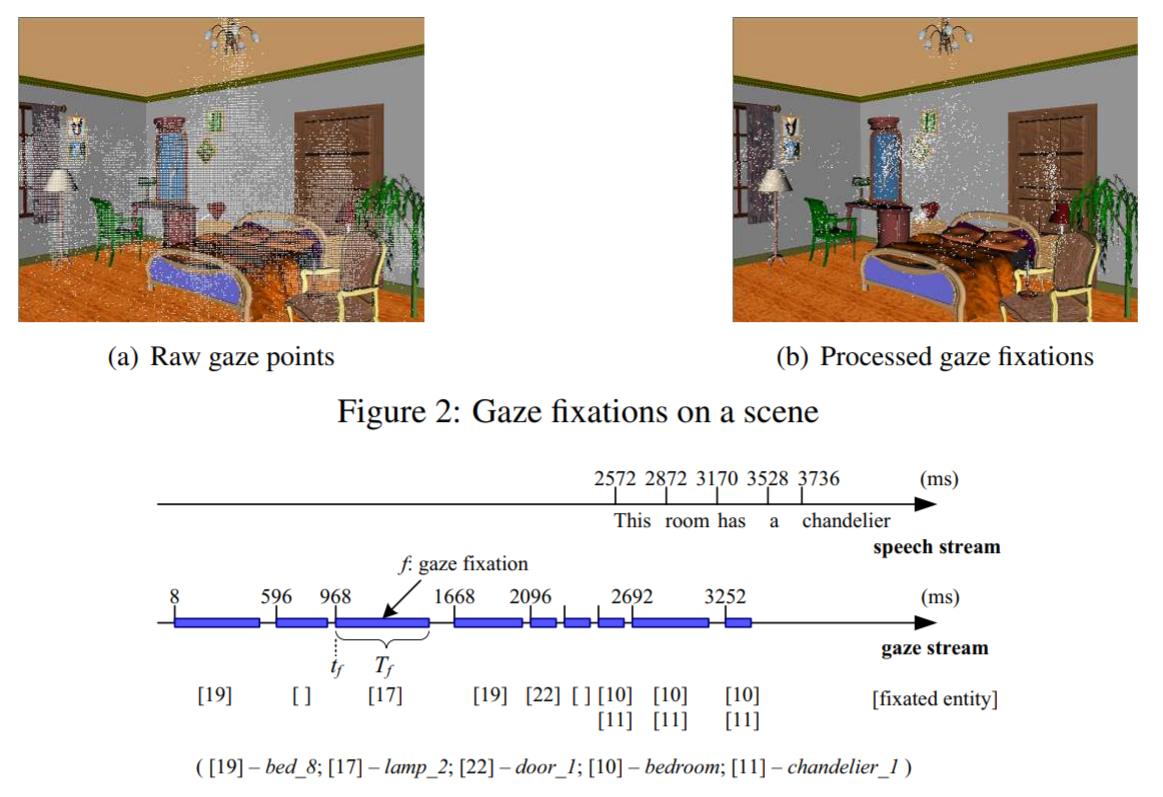
user<id>.xmlIn each user folder, automatically segmented utterances with accompanying gaze fixations, and annotation of referred entities in the utterances.
An example:
<user_input> <gaze> <selection> <entity text="chair_green">0.190656</entity> <entity text="door">0.069329</entity> <entity text="lamp_bank">0.229842</entity> <entity text="dresser">0.510173</entity> </selection> </gaze> <speech> <entity_annotation>chair_green</entity_annotation> <transcription>I like the fact that there's a chair in front of the</transcription> <waveform>wav\2_5100_4190.wav</waveform> </speech> </user_input>In the above example, 4 objects (contained in
<selection/>tag) were fixated by the user while speaking the utterance. Each fixated object is associated with a probability that is calculated based on temporal length of the gaze fixations. The entity referred by the user’s utterance is objectchair_green(contained in<entity_annotation/>tag). -
user<id>_speech.xmlTimestamped tokens of the speech transcript.
-
fixation_<id>.txtGaze fixations of user. In the fixation file, the numbers contained in
[]are the fixated object ids.
Cite Us
This data was used in the following papers:
- S. Qu and J. Chai. Incorporating Temporal and Semantic Information with Eye Gaze for Automatic Word Acquisition in Multimodal Conversational Systems. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 244-253, 2008.
- S. Qu and J. Chai. An Exploration of Eye Gaze in Spoken Language Processing for Multimodal Conversational Interfaces. In Proceedings of the Conference of the North America Chapter of the Association of Computational Linguistics (NAACL), pages 284-291, 2007.