Implicit Arguments in Nominal Semantic Role Labeling
Motivations and Objectives
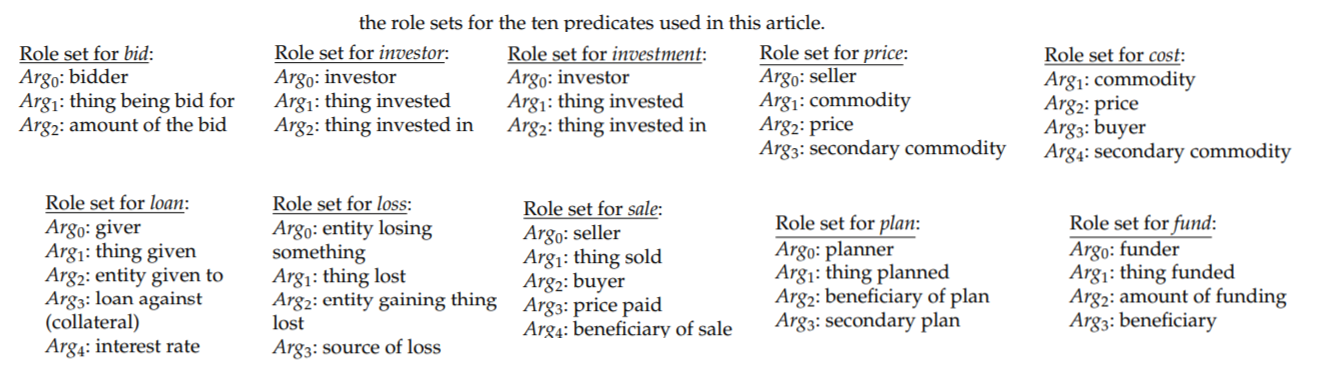
Across the internet, a significant amount of information resides in non-spoken, unstructured language repositories such as news articles, Wikipedia, and weblogs. The goal of semantic role labeling is to uncover the basic semantic structure of these texts by identifying events and event participants. Traditional research in this area has focused on events denoted by verbal predicates. Furthermore, the scope of participant identification has usually been restricted to the sentence containing the predicate of interest. This project extends traditional semantic role labeling in two important ways. First, it investigates semantic role labeling for nominal (i.e., noun-based) predicates, which are prominent carriers of semantic information. Second, it relaxes the scope of participant identification to include all sentences in a textual discourse. Together, these two extensions provide a more complete account of textual meaning and discourse coherence.
Related Papers
-
Semantic Role Labeling of Implicit Arguments for Nominal Predicates. M. Gerber and J. Y. Chai. Computational Linguistics, vol. 38, issue 4, Pages 755-798, November 2012.
-
Semantic Role Labeling of Implicit Arguments for Nominal Predicates. M. Gerber, Ph.D. Dissertation, 2011.
-
Beyond NomBank: A Study of Implicit Arguments for Nominal Predicates. M. Gerber and J. Y. Chai. Proceedings of the Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics.. Uppsala, Sweden. July 2010. (Best Long Paper Award)
-
The Role of Implicit Argumentation in Nominal SRL. M. Gerber, J. Y. Chai, and A. Meyers. Proceedings of the Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Boulder, CO, USA. June, 2009.